
Flowchief, the SCADA system for distribution grids
FlowChief is a software based solution for network control engineering. It is a network control system designed for monitoring, control and optimization of power grids. It offers features such as:
- Monitoring of the current flow in the network
- Network stability monitoring
- Power distribution control
- Management and monitoring of control equipment
- Monitoring of power production and consumption
- Monitoring and management of energy exchange between networks
- Monitor and control the deployment of transmission and distribution networks.
These functions make it possible to operate the power grid more efficiently and safely, avoid faults and increase the efficiency of the grid.

I am a registered partner of Flowchief and therefore I can offer you project realization, implementation of software or changes in existing system.
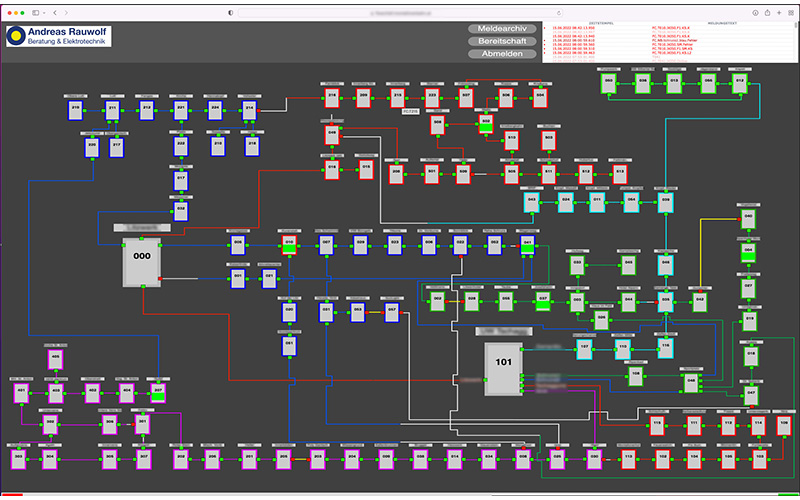
Flowchief is a PC-based system and is very well suited for economical monitoring of the distribution network:
- Graphical representation of the network status using an interactive network map
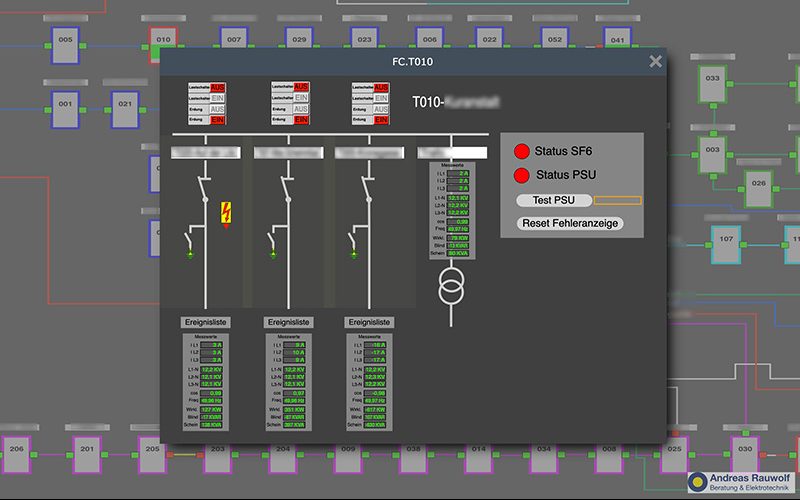
- Detail view transformer station
- Message archive with note function
- Alerting functions with on-call schedules
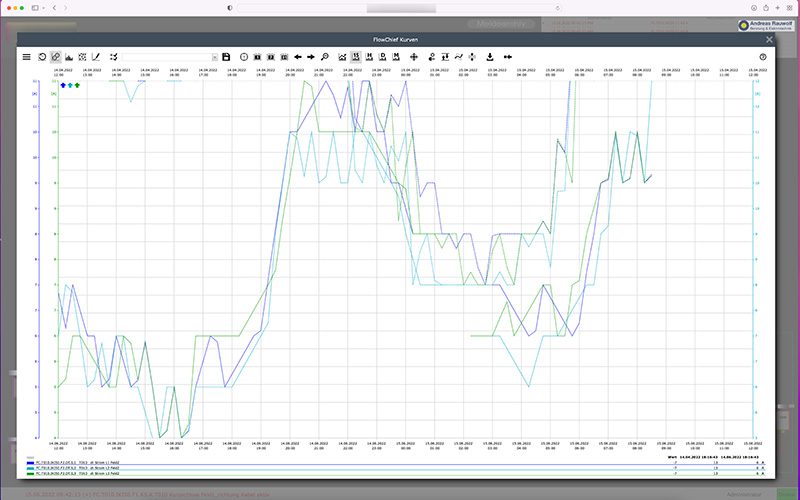
- Measured value curves
- Parameterizable by the customer
- Slim design
- Expandable
- Manufacturer-independent
- Supports very many communication protocols
Your contact for the Flowchief network control system

Do you have questions about Flowchief? You can reach me via my contact form or by email and phone:
Dipl. Ing. Andreas Rauwolf
E-mail: info(at)rauwolf-beratung.de
Tel.: +49 711 912 714 20
Content supplemented with AI
What is a network control system?
A grid control system is a computerized system used to monitor, control, and optimize an electrical power grid. It enables monitoring of power flow, monitoring of network stability and control of power distribution to avoid disturbances and increase the efficiency of the network.
What is network control technology?
Network control technology in the power grid is used to monitor, regulate and control the flow of electricity in the grid in order to prevent faults and ensure a safe and efficient power supply. This includes:
- Monitoring of network operation, including voltage, current and frequency
- Monitoring and control of power plant energy production
- Monitoring and regulation of energy demand and consumption
- Monitoring and management of energy exchange between different networks
- Monitor and control the use of control equipment such as transmission and distribution networks.
The aim of network control technology is to ensure a safe, efficient and reliable energy supply for customers.
What are digital power grids and smart grids?
Electricity distribution networks have changed drastically in recent years due to the integration of renewable energies: The requirements for fail-safety, monitoring and control of the grids have increased. Digital power grids, smart grids and fault detection are just some of the keywords.
Transformer station as digital node in smart grids
Until a few years ago, a transformer station typically consisted of the transformer plus locally operable medium-voltage switchgear and LV distribution. With increased requirements for transparency and fail-safety, a digital transformer station in the smart grid consists of diverse sensor technology and digital communication.
Fault detection and ground fault detection, fast fault declaration
In the event of a fault, reliable short circuit detection and ground fault detection is critical. But which method should be used specifically for ground fault direction detection as a function of star point grounding? Which fault detection is suitable for your network? I advise you independently and with technical depth.
Digital power grids, smart grid and fault detection: independent consulting, installations and commissioning
As an electricity grid operator, do you need a vendor-independent view of your grids and a strategy for becoming a smart grid?
Do you want to optimize your SAIDI by reducing downtime and need assistance in selecting the appropriate short-circuit detection and ground-fault detection methods?
Do you need instruction for your team in setting up and operating the new measuring and recording technology in the transformer stations or a complete service for installation and commissioning?
Remote transmission and telecontrol
The measurement data is recorded on site, the errors are reliably determined, and now? How does this information get to the places that need it without delay, safely and reliably?
I will advise you on the selection of suitable remote transmission technology and communication protocols.
The distribution network
The distribution network is part of the electrical power supply system and is used to transport electricity from the transmission networks to the end users. It consists of distributors, transformers and lines that reduce the current to lower voltages and deliver it directly to consumers. Tasks of the distribution network are:
- Transfer of current to lower voltages
- Distribution of electricity to consumers
- Monitoring and regulation of the current flow
- Monitoring and rectification of faults in the network
- Support for the integration of renewable energy sources
- Providing energy for public services such as street lighting.
The distribution network plays an important role in ensuring a safe, reliable and efficient energy supply for consumers.

